


The homologous regions inside homologous chromosome pairs begin to associate with each other. In the state it consists of two sister chromatids. It is based on chromosomes that begin to condense. The Leptotene is the first stage of prophase I. This prophase I are occurs at different speed based on the species and sex. In mitotic prophase many of the events occur inside these phases such as pairing of homologous chromosomes and then the reciprocal exchange of genetic material within these homologous chromosomes. The five stages of prophase I are leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, diakinesis. Prophase I is the most complex phase in all meiosis because it is a homologous chromosome and must pair and exchange genetic information. This meiosis involves two rounds of chromosome segregation and then it undergoes prophase twice and thus resulting in prophase I and prophase II. No crossing over occurs between sister chromatids.Hint: It is the first stage of cell division in both the mitosis and meiosis. After crossing over, it could contain genes for blue eyes and brown hair, by taking the gene for blue eyes from one of the chromatids of that chromosome's homolog (see figure right). For example, suppose one chromatid of a chromosome initially contained genes for brown eyes and brown hair. As a result, the gene combinations on a chromosome can be changed. During this process of synapsis the two chromosomes of each homolog pair exchange segments of DNA in a process known as crossing over.
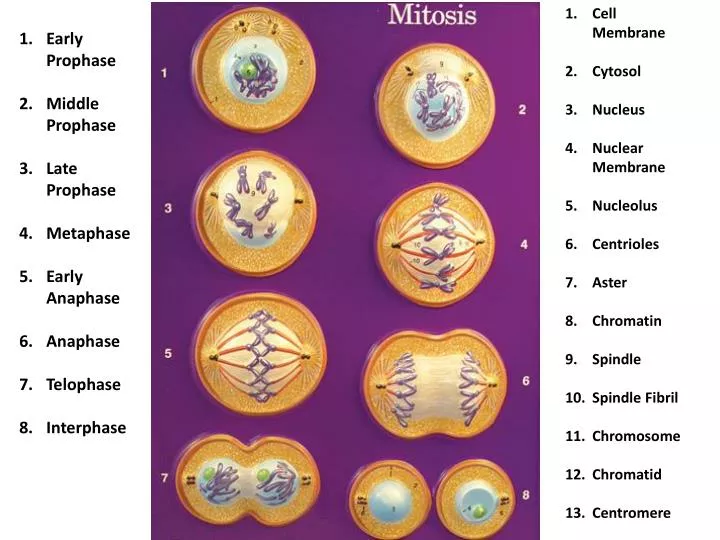
When the chromosomes synapse during prophase I, each gene in each chromosome is brought into contact with the same gene on that chromosome's homolog. Normally, the two chromosomes making up a homolog pair are not genetically identical - as is the case with sister chromatids - because homologs are inherited from different parents. Some other bio-terms starting with pro: prognosis, prokaryote, pronucleus.Ĭrossing over. The name prophase is derived from the Latin word pro, meaning before. Only later do they become separately visible. Early on during prophase, the two chromosomes of which a tetrad is composed fuse together so tightly that they cannot be distinguished from each other, which is called synapsis. But the appearance of a tetrad changes in the different substages of prophase I ( read about these substages >). This is to show that the two chromosomes of each homolog pair adhere to each other during this phase of meiosis. In the upper diagram two tetrads are represented as two x-shaped chromosomes associated side by side. During most of meiosis (through the end of metaphase II) the sister chromatids remain attached to each other at the centromere.ĭuring prophase I the two members of each homolog pair become intimately associated along their entire lengths (that is, they "synapse") to form a structure known as a tetrad (or bivalent). Also, the spindle apparatus (yellow strands in the diagram) begins to extend outward from the two centrosomes, which move to the opposite ends ("poles") of the cell.Įach chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids containing identical genetic information. The chromosomes (shown in red) become visible as they shorten, coil, and thicken (that is, as they "condense"). So crossing-over between both of the synapsed chromatid pairs does occur.ĭuring this phase of meiosis, the nuclear envelope (shown in white in the diagram at right) breaks up and disappears. Note that while crossing over is shown here, for simplicity, between only one of the two chromatids of each chromosome, each chromatid of each chromosome actually synapses with one of the chromatids of that chromosome's homolog.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
